These of us who had been residing within the US in 2013 could keep in mind when HealthCare.gov, a brand new (and at the moment, controversial) on-line market for medical health insurance, was launched by the US authorities and crashed inside two hours. A subsequent examine by the Authorities Accountability Workplace discovered that the web site had been developed “with out efficient planning” and that “key technical necessities had been unknown.” Person demand had additionally been severely underestimated. Primarily, lots of the web site’s failures had been resulting from poor product necessities planning.
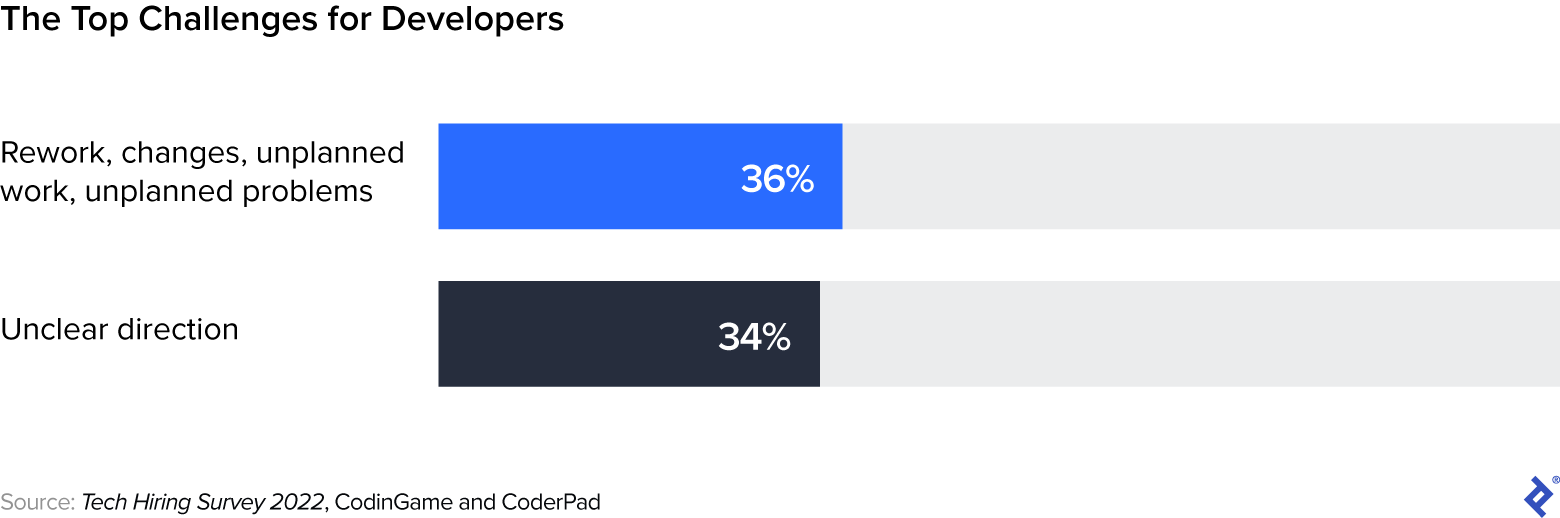
Necessities gathering is an important a part of product improvement—and it’s additionally the stage at which product leaders typically go flawed. Quite a few research level to ineffective necessities gathering as a supply of main points for developer productiveness. In an intensive 2022 survey by CodinGame and Coderpad, for instance, the principle challenges for software program builders had been cited as “rework, modifications, unplanned work, unplanned issues” and “unclear path.” These challenges may be mitigated by implementing a sturdy necessities gathering course of.
As a senior program, undertaking, and product supervisor, I’ve witnessed a broad vary of attitudes towards necessities gathering by corporations and groups, a few of which have finally resulted in wasted assets, scope creep, upset clients, and underperforming merchandise. On this article, I’ll unpack a number of of those errors and establish key learnings as a way to keep away from making these identical errors.
Frequent Biases to Keep away from Throughout Necessities Gathering
One of many key challenges at any stage of the event course of just isn’t letting inherent biases affect our work. Because of this a sturdy, goal necessities gathering course of is important.
Analysis by famend undertaking administration professional Bent Flyvbjerg reveals a number of frequent biases that always come up in undertaking administration. In my expertise, these identical biases may affect the early phases of product improvement. These are those you need to be careful for:
|
Bias |
Manifestation |
|---|---|
|
Strategic misrepresentation |
The tendency to intentionally and systematically distort or misstate info for strategic functions (also called political bias, strategic bias, or energy bias) |
|
Optimism bias |
The tendency to be overly optimistic concerning the consequence of deliberate actions, together with overestimation of the frequency and dimension of constructive occasions, and underestimation of the frequency and dimension of unfavorable occasions |
|
Uniqueness bias |
The tendency to see your undertaking as extra singular than it really is |
|
Planning fallacy |
The tendency to underestimate prices, schedule, and threat, and overestimate advantages and alternatives
|
|
Overconfidence bias |
The tendency to have extreme confidence in your individual solutions to questions |
|
Hindsight bias |
The tendency to see previous occasions as being predictable on the time these occasions occurred |
|
Availability bias |
The tendency to overestimate the chance of occasions with better ease of retrieval (availability) in reminiscence |
|
Base-rate fallacy |
The tendency to disregard generic base-rate info and give attention to particular info pertaining to a sure case or small pattern |
|
Anchoring |
The tendency to rely too closely on one trait or piece of data when making selections, usually the primary piece of data acquired on the related matter |
|
Escalation of dedication |
The tendency to justify elevated funding in a choice, primarily based on the cumulative prior funding, regardless of new proof suggesting the choice could also be flawed; also called the sunk-cost fallacy |
5 Ineffective Approaches to Necessities Gathering
The necessities gathering course of will look totally different for each firm and product, and there are a number of approaches you may take that can result in a profitable consequence. Fairly than speaking about what to do, it’s extra environment friendly to explain frequent missteps that can have a unfavorable affect on product outcomes. Listed here are the highest 5 errors to keep away from throughout necessities gathering:
1. Defining a Product by What It Isn’t
A couple of years in the past I used to be on a workforce dealing with an organization intranet portal improve. The client’s objective was easy: Design a brand new portal that does not resemble the earlier failed product. (The corporate had just lately tried to replace the portal however the ultimate resolution had been rejected by the tip customers.) At first look, “Not like X” may appear to be a fantastic requirement. However the workforce’s response was to give attention to the visuals, preserving the identical options and re-releasing the product with a brand new colour and branding. After all, this product encountered the identical points because the earlier one as a result of its options and performance remained largely unchanged. The issue wasn’t the colour or branding—it was that the product necessities had not been redefined.
Lesson: Necessities gathering just isn’t elective; you may’t wing it, and there aren’t any shortcuts. Altering the feel and appear of a product received’t clear up its underlying issues. And you need to by no means outline a product solely by what it shouldn’t be.
2. Copying Your Competitor
A midsize firm sees a competitor has taken benefit of a possibility out there, and it needs in on the motion. Pace to market is important, so no time may be spared to assemble necessities. As a substitute, the workforce merely copies product options from its competitor. The client’s response is: “The place are the assist options on this product that we worth in your different merchandise?” and “How does this product combine with the opposite merchandise we now have already bought from you?” The shortage of a coherent reply to those questions leads to a annoyed product workforce and unhappy clients.
Lesson: You aren’t your rivals. You’ll be able to’t construct a duplicate product and anticipate your clients to leap on board. When gathering product necessities, at all times take into consideration the wants of your particular clients and why they like your current merchandise. Ask your self how one can combine the worth you provide as an organization into this new product.
3. Not Partaking With Prospects
I used to be as soon as on a workforce at a brand new firm that had constructed a product with wonderful options that outperformed the competitors. Sadly, the workforce forgot one important factor within the necessities gathering course of: the shopper. In actual fact, they had been petrified of participating with them, leery of unfavorable suggestions, and afraid of a poor product-market match being revealed. Thus, the set of product necessities that they had developed lacked important buyer enter.
4. Creating Pointless Options
As product managers, we have to be specialists on our clients’ wants. If the providers your organization supplies are B2B, you will need to even perceive your clients’ clients. Success is the shopper wanting what they get. With a purpose to know what your clients need, you may analyze stories, learn articles, and attend conferences—however to achieve the clearest perception, it’s essential to ask them what they need.
I’ve discovered this lesson myself the onerous approach. On one undertaking, we had engaged with clients and different stakeholders and developed a listing of product necessities. Nonetheless, when it was time for me to create person tales, I didn’t affirm each with the shopper. I believed they wouldn’t care a few back-end logging function or a minor Kubernetes infrastructure node configuration change—mainly, something that wasn’t UI- or UX-based. However I used to be flawed. One particular buyer was obsessive about all of the options in our product and needed to find out about each layer of its performance, and even had new concepts for helpful options.
Lesson: Don’t assume a buyer’s stage of curiosity. Get into the specifics with them. Usually, clients are extra curious than we expect. As a product supervisor, you may find yourself delivering a function the shopper doesn’t need, and never correctly delivering on the options they do need, since you didn’t ask them what they thought.
5. Believing Agile Is the Solely Means
Not too long ago, I used to be on a workforce at a big IT providers firm delivering a buyer engagement product. The product scope was {that a} small workforce of consultants would go to the shopper’s web site, deploy our proprietary software program evaluation product, and analyze the shopper’s community for cloud connectivity points and alternatives. After the service was delivered, a report can be despatched to the shopper. It was a easy Waterfall product supply with fastened deliverables, timing, and prices. A couple of hours into the on-site supply, the shopper discovered different community points that didn’t contain the know-how we had agreed to scan. “Let’s be agile,” they mentioned, and requested us to vary our product to research the printers, firewalls, and consumer connectivity points. The product necessities had already been agreed upon, nevertheless, and we would have liked to forestall scope creep. We opted to ship the present product, then take the brand new buyer requests and use these as necessities for a future model.
Lesson: Agile is one technique to handle a services or products, however not the one approach. At a sure level it’s essential to finalize the necessities and transfer on to the following stage. How are you aware once you’re finished gathering necessities? It’s easy: when the necessities have been agreed upon with the shopper—and no later. You need to use Agile to develop your undertaking, however you need to make use of a Waterfall-style supply. Generally one of the best reply to the shopper is, “Let’s speak about that on our subsequent engagement,” or “We wish you to understand worth as quickly as attainable, so let’s not get distracted by new necessities proper now.”
Implement These Classes for a Sturdy Strategy
Necessities gathering is a crucial stage within the improvement of any product and shouldn’t be ignored. The premise for a product can’t be what you don’t need it to be, nor ought to it merely be a replication of one thing already available on the market. Interact along with your innovator and early-adopter buyer base to get their precious insights, and don’t be afraid of asking questions to make sure you’re not losing time constructing pointless options. Know when to finalize the necessities and transfer on, or use a Waterfall strategy for supply. Implement these classes for necessities gathering on the outset of your initiatives for productive groups, comfortable clients, and profitable outcomes.
