One in every of my shoppers relocated their web site to a bulk internet hosting account. They up to date their area’s DNS settings for the A and CNAME data however had been having problem figuring out whether or not the positioning was resolving with the brand new internet hosting account (new IP Handle).
When troubleshooting DNS, have in mind a number of issues: Perceive how DNS works, perceive how your area registrar works, and perceive how your host manages its area entry.
How DNS Works
Whenever you kind a site right into a browser:
- The area is seemed up in an Web title server to find the place the request ought to be despatched to.
- Within the case of an internet area request (http), a reputation server will return the IP tackle to your pc.
- Your pc then shops this regionally, often called your DNS Cache.
- The request is shipped to the host, which routes the request internally and presents your web site.
How Your Area Registrar Works
Word: Not each area registrar truly manages your DNS. I’ve one shopper, for instance, who registers their domains by means of Yahoo! Regardless of showing to take action of their administration, Yahoo! is only a reseller for Tucows. Consequently, if you change your DNS settings in Yahoo!, it could take hours earlier than these adjustments are up to date within the actual area registrar.
When your DNS settings get up to date, they’re propagated throughout an array of servers throughout the Web. More often than not, this takes a number of seconds to occur. That is one purpose why individuals can pay for managed DNS. Managed DNS corporations usually have each redundancy and are extremely quick… usually quicker than your area registrar.
As soon as the Web servers are up to date, the subsequent time your system makes the DNS request, the IP tackle the place your web site is hosted is returned. NOTE: Do not forget that I mentioned the subsequent time your system makes the request. Should you beforehand requested that area, the Web might be updated, however your native system could also be resolving an previous IP tackle based mostly in your DNS Cache.
How Your Host DNS Works
The IP tackle returned and cached by your native system isn’t usually distinctive to a single web site. A bunch could have dozens and even a whole bunch of internet sites hosted on a single IP Handle (usually a server or digital server). So, when your area is requested from the IP Handle, your host forwards your request to the particular folder location throughout the server and presents your web page.
Tips on how to Troubleshoot DNS
As a result of there are three programs right here, there are additionally three programs to troubleshoot! First, you’ll need to test your native system to see the place the IP Handle is pointing to in your system:
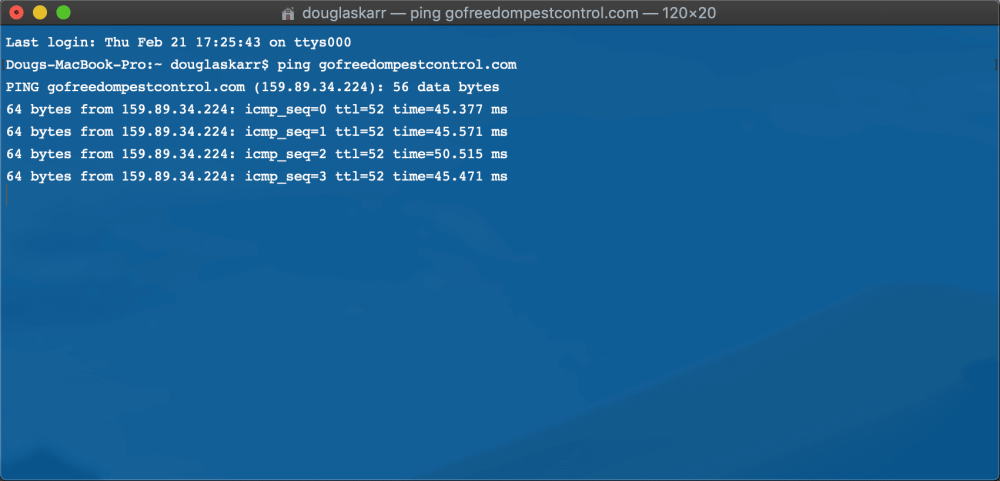
That is completed simply by opening a Terminal window and typing:
ping area.comOr you are able to do a particular title server lookup:
nslookup area.com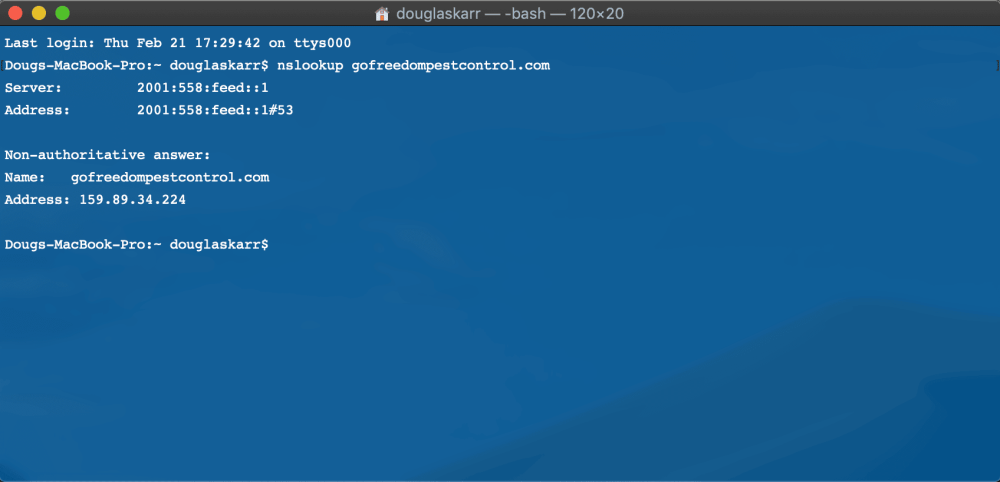
Should you’ve up to date the DNS settings in your area registrar, then you definitely’ll need to guarantee your DNS cache is cleared, and also you’ll need to make the request once more. To clear your DNS cache in macOS:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
sudo killall mDNSResponderHelper
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache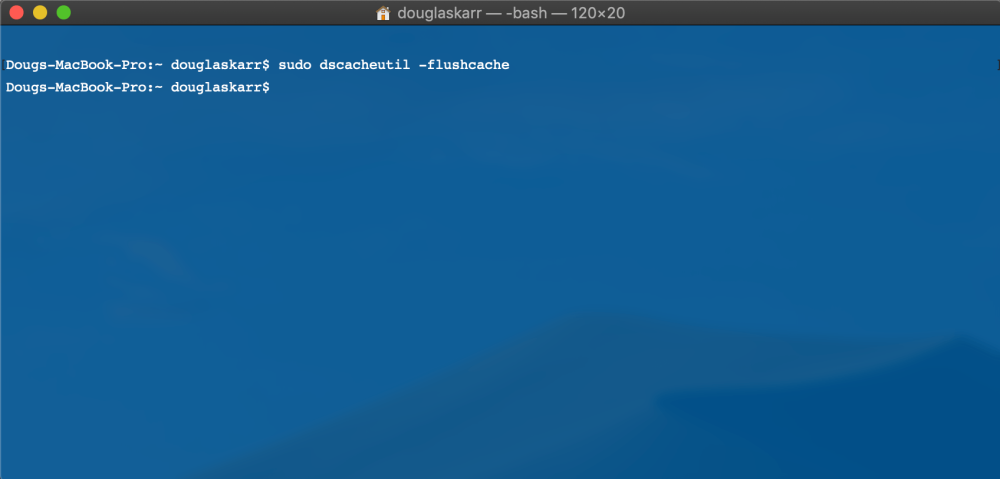
At this level, you possibly can retry the ping or nslookup to see if the area resolves to a brand new IP tackle.
The following step can be to see if the Web’s DNS servers have been up to date. Hold DNSstuff helpful for this: you may get a full DNSreport by means of their platform that’s actually good.
Should you see the IP tackle correctly displayed throughout the online and your web site remains to be not exhibiting up, you possibly can bypass the Web’s servers and inform your system simply to ship the request on to the IP Handle. You possibly can accomplish this by updating your hosts file and flushing your DNS. To do that, open Terminal and sort:
sudo nano /and so on/hosts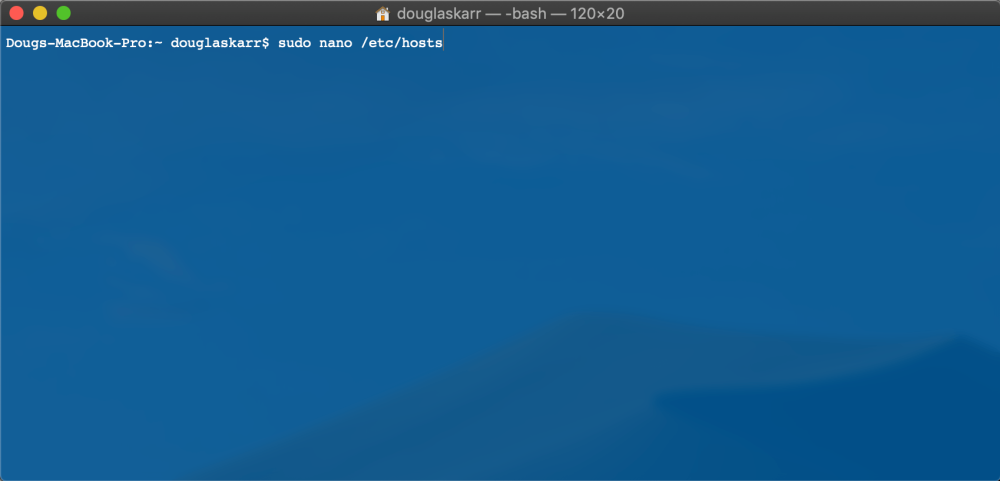
Enter your system password and press enter. That may convey up the file straight in Terminal for enhancing. Transfer your cursor utilizing your arrows and add a brand new line with the IP tackle adopted by the area title.
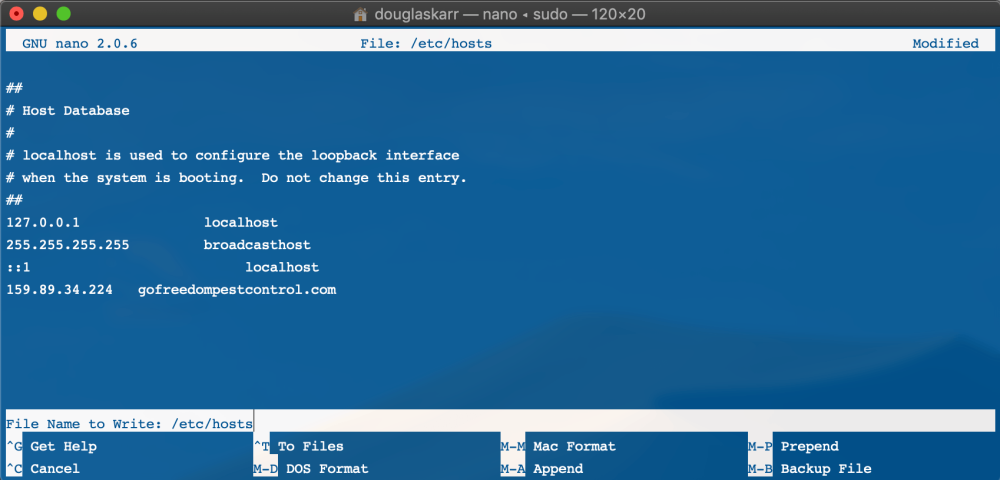
Press control-o in your keyboard to avoid wasting the file, then return to just accept the filename. Exit the editor by urgent control-x, which can return you to the command line. Don’t overlook to flush your cache. If the positioning doesn’t come up okay, it could be an issue native to your host, and you must contact them and allow them to know.
Final notice: Bear in mind to return your hosts file to its authentic model. You don’t need to go away an entry that you just need to replace mechanically!
By following these steps, I used to be capable of confirm that my the DNS entries within the registrar had been updated, the DNS entries on the Web had been updated, my Mac’s DNS cache was updated, and the online host’s DNS was updated… good to go!
