30-second abstract:
- Content material managers who need to assess their on-page efficiency can really feel misplaced at sea as a consequence of quite a few Search engine marketing indicators and their perceptions
- This drawback will get larger and extremely advanced for industries with area of interest semantics
- The eventualities they current to the content material planning course of are extremely particular, with distinctive lexicons and semantic relationships
- Sr. Search engine marketing Strategist at Brainlabs, Zach Wales, makes use of findings from a rigorous aggressive evaluation to make clear how you can consider your on-page sport
Industries with area of interest terminology, like scientific or medical ecommerce manufacturers, current a layer of complexity to Search engine marketing. The eventualities they current to the content material planning course of are extremely particular, with distinctive lexicons and semantic relationships.
Search engine marketing has many layers to start with, from technical to content material. All of them intention to optimize for quite a few search engine rating indicators, a few of that are shifting targets.
So how does one method on-page Search engine marketing on this difficult house? We not too long ago had the privilege of conducting a prolonged aggressive evaluation for a consumer in one in every of these industries.
What we walked away with was a repeatable course of for on-page evaluation in a sophisticated semantic house.
The problem: Turning findings into motion
On the outset of any evaluation, it’s necessary to outline the problem. In probably the most common sense, ours was to show findings into significant on-page actions — with priorities.
And we might do that by evaluating the key phrase rating efficiency of our consumer’s area to that of its 5 chosen opponents.
Particularly, we wanted to establish areas of the consumer’s web site content material that have been dropping to opponents in key phrase rankings. And to prioritize issues, we wanted to indicate the place these losses have been having the best influence on our consumer’s potential for search visitors.
Including to the complexity have been two further sub-challenges:
- Quantity of key phrase information. When folks consider “area of interest markets,” the implication is often a small variety of key phrases with low month-to-month search volumes (MSV). Scientific industries will not be so. They’re “area of interest” within the sense that their semantics will not be accessible to all—together with key phrase analysis instruments—however their depth & breadth of key phrase potential is huge.
- Our consumer already dominated the market. At first look, utilizing key phrase hole evaluation instruments, there have been no product classes the place our consumer wasn’t dominating the market. But they have been incurring visitors losses from these 5 opponents from a seemingly random, spread-out variety of circumstances. Taken collectively incrementally, these losses had vital impacts on their internet visitors.
If the needle-in-a-haystack analogy involves thoughts, you see the place that is going.
To place the main points to our problem, we needed to:
- Establish the place these incremental results of key phrase rank loss have been being felt probably the most — understanding this may information our prioritization;
- Map these key phrase developments to their respective stage of the advertising and marketing funnel (from informational top-of-funnel to the transactional bottom-of-funnel)
- Rule out off-page components like backlink fairness, Core Net Vitals & web page pace metrics, to be able to…
- Isolate circumstances the place competitor pages ranked larger than our consumer’s on the deserves of their on-page strategies, and at last
- Establish what these profitable on-page strategies have been, in hopes that our consumer may adapt its content material to a profitable on-page system.
Easy methods to spot developments in a sea of information
When the information units you’re working with are massive and no obvious developments stand out, it’s not as a result of they don’t exist. It solely means you need to alter the best way you take a look at the information.
As a disclaimer, we’re not purporting that our method is the one method. It was one which made sense in response to a different problem at hand, which, once more, is one which’s frequent to this business: The intent measures of Search engine marketing instruments like Semrush and Ahrefs — “Informational,” “Navigational,” “Industrial” and “Transactional,” or some mixture thereof — will not be very dependable.
Our method to recognizing these developments in a sea of information went like this:
Step 1. Break it right down to short-tail vs. lengthy tail
Numbers don’t lie. Absent dependable intent information, we reduce the dataset in half primarily based on MSV ranges: Key phrases with MSVs above 200 and people equal to/beneath 200. We even graphed these out, and certainly, it returned a basic brief/long-tail curve.

This gave us a proxy for funnel mapping: Quick-tail key phrases, outlined as high-MSV & broad focus, might be principally related to the higher funnel. This made long-tail key phrases, being much less searched however extra particularly targeted, a proxy for the decrease funnel.
Doing this additionally helped us handle the million-plus key phrase dataset our instruments generated for the consumer and its 5 competitor web sites. Even in the event you carry out the export hack of downloading information in batches, neither Google Drive nor your system’s RAM need something to do with that a lot information.
Step 2. Set up an inventory of keyword-operative root phrases
The “keyword-operative root phrase” is the time period we gave to root phrases which might be frequent to many or all the key phrases below a sure subject or content material kind. For instance, “dna” is a typical root phrase to many of the key phrases about DNA lab merchandise, which our consumer and its opponents promote. And “protocols” is a root phrase for a lot of key phrases that exist in upper-funnel, informational content material.
We established this checklist by putting our short- and long-tail information (exported from Semrush’s Key phrase Hole evaluation instrument) into two spreadsheets, the place we have been capable of view the shared key phrase rankings of our consumer and the 5 opponents. We outfitted these spreadsheets with information filters and formulation that scored every key phrase with a aggressive worth, relative to the six internet domains analyzed.
Individually, we took an inventory of our consumer’s product classes and brainstormed all potentialities for keyword-operative root phrases. Lastly, we filtered the information for every root phrase and famous developments, such because the variety of key phrases {that a} web site ranked for on Google web page 1, and the sum of their MSVs.
Lastly, we utilized a calculation that included common place, MSV, and business click-through charges to quantify the importance of a development. So if a competitor appeared to have a key phrase rating edge over our consumer in a sure subset of key phrases, we may place a numerical worth on that edge.
Step 3. Establish content material templates
If one in every of your aims is to map key phrase developments to the advertising and marketing funnel, then it’s vital to grasp the position of web page templates. Why?
Web page pace efficiency is a recognized rating sign that must be thought of. And ecommerce web sites usually have content material templates that mirror every stage of the funnel.
On this case, all six opponents conveniently had distinct templates for top-, middle- and bottom-funnel content material:
- High-funnel templates: Textual content-heavy, informational content material in what was generally referred to as “Studying Sources” or one thing related;
- Center-funnel templates: Additionally text-heavy, informational content material a couple of product class, with hyperlinks to merchandise and visible content material like diagrams and movies — the Product Touchdown Web page (PLP), basically;
- Backside-funnel templates: Transactional, Product Element Pages (PDP) with concise, conversion-oriented textual content and buying calls-to-action.
Step 4. Map key phrase developments to the funnel
After cross-examining the basis phrases (Step 2), key phrase rating developments started to emerge. Now we simply needed to map them to their respective funnel stage.
Having recognized content material templates, and having the information divided by short- & long-tail made this a faster course of. Our major focus was on developments the place competitor webpages have been outranking our consumer’s website.
Figuring out content material templates introduced the added worth of seeing the place opponents, for instance, outranked our consumer on a sure key phrase as a result of their profitable webpage was in-built a content-rich, optimized PLP, whereas our consumer’s lower-ranking web page was a PDP.
Step 5. Rule out the off-page rating components
Since our objective was to establish & analyze on-page strategies, we needed to rule out off-page components like hyperlink fairness and web page pace. We sought circumstances the place one web page outranked one other on a shared key phrase, regardless of having inferior hyperlink fairness, web page pace scores, and so on.
For all of Google’s developments in processing semantics (e.g., BERT, the Useful Content material Replace) there are nonetheless circumstances the place a web page with skinny textual content content material outranks one other web page that has lengthier, optimized textual content content material — by advantage of hyperlink fairness.
To rule these components out, we assigned an “Search engine marketing scorecard” to every webpage below investigation. The scorecard tallied the variety of rank-signal-worthy attributes the web page had in its Search engine marketing favor. This included issues like Semrush’s web page authority rating, the variety of inner vs. exterior inlinks, the presence and forms of Schema markup, and Core Net Vitals stats.
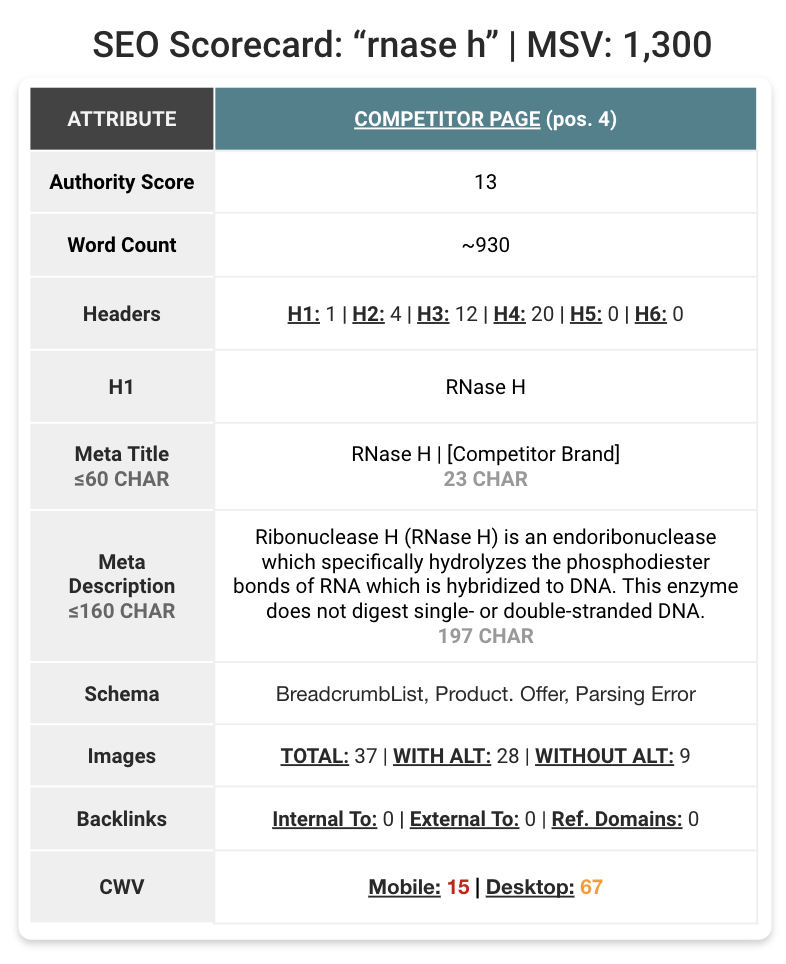
The scorecards additionally included on-page components, just like the variety of headers & subheaders (H1, H2, H3…), use of key phrases in alt-tags, meta titles & their character counts, and even web page phrase depend. This helped give a high-level sense of on-page efficiency earlier than diving into the content material itself.
Our findings
When evaluating the Search engine marketing scorecards of our consumer’s pages to its opponents, we solely selected circumstances the place the dropping scorecard (in off-page components) was the key phrase rating winner. Listed below are just a few of the standout findings.
Including H3 tags to merchandise names actually works
This month, OrangeValley’s Koen Leemans printed a Semrush article, titled, Search engine marketing Break up Check Consequence: Including H3 Tags to Merchandise Names on Ecommerce Class Pages. We discovered this examine particularly well-timed, because it validated what we noticed on this aggressive evaluation.
To these versed in on-page Search engine marketing, putting key phrases in <h3> HTML format (or any stage of <h…> for that matter) is a smart transfer. Google crawls this textual content earlier than it will get to the paragraph copy. It’s a recognized rating sign.
On the subject of Search engine marketing-informed content material planning, ecommerce purchasers tend — coming from the very best of intentions — to forsake the product title in pursuit of the right on-page recipe for a particular non-brand key phrase. The worth of the product title turns into a blind spot as a result of the model assumes it’s going to outrank others by itself product names.
It’s someplace on this thought course of that an editor might, for instance, determine to checklist product names on a PLP as bolded <p> copy, reasonably than as a <h3> or <h4>. This, apparently, is a missed alternative.
Extra thus far, we discovered that this on-page tactic carried out even higher when the <h>-tagged product title was linked (index, comply with) to its corresponding PDP, AND accompanied with a sentence description beneath the product title.
That is in distinction to the product touchdown web page (PLP) which has ample supporting web page copy, and solely lists its merchandise as hyperlinked names with no descriptive textual content.
Phrase depend in all probability issues, <h> depend very probably issues
Within the ecommerce house, it’s not unusual to search out PLPs that haven’t been visited by the content material fairy. A storyless grid of photos and product names.
But, in each case the place two PLPs of this selection went toe-to-toe over the identical key phrase, the sheer variety of <h> tags gave the impression to be the one on-page issue that ranked one PLP above its opponents’ PLPs, which themselves had larger hyperlink fairness.
The takeaway right here is that if you received’t have time to the touch up your PLPs with touchdown copy, you need to at the least set all product names to <h> tags which might be hyperlinked, and enhance the variety of them (e.g., set the web page to load 6 rows of merchandise as a substitute of 4).
And phrase depend? Though Google’s John Mueller confirmed that phrase depend is just not a rating issue for the search algorithm, this subject is debated. We can not enterprise something conclusive about phrase depend from our aggressive analyses. What we are able to say is that it’s a element of our discovering that…
Defining your complete subject along with your content material wins
Backlinko’s Brian Dean ventured and proved the radical notion which you can optimize a single webpage to rank for not the same old 2 or 3 goal key phrases, however a whole lot of them. That’s in case your copy encompasses all the things in regards to the subject that unites these a whole lot of key phrases.
That apply may fit in long-form content material advertising and marketing however is rather less relevant in ecommerce settings. The choice to that is to create a physique of pages which might be all interlinked intentionally and logically (from a UX standpoint) and that cowl each side of the subject at hand.
This content material ought to tackle the questions that individuals have at every stage of the awareness-to-purchase cycle (i.e., the funnel). It ought to outline area of interest terminology and spell out acronyms. It must be accessible.
In a single stand-out case from our evaluation, a competitor web page held place 1 for a profitable key phrase, whereas our consumer’s website and that of the opposite opponents couldn’t even muster a web page 1 rating. All six web sites have been addressing the key phrase head-on, arguably, in all the suitable methods. They usually had superior hyperlink fairness.
What did the winner have that the remainder didn’t? It occurred that on this lone occasion, its product was being marketed to a high-school instructor/administrator viewers, reasonably than a PhD-level, company, governmental or college scientist. By this advantage alone, their advertising and marketing copy was much more layman-accessible, and, apparently, Google accredited too.
The takeaway is to not dumb-down the mandatory jargon of a technical business. But it surely highlights the necessity to inform each a part of the story inside a subject vertical.
Conclusion: Findings-to-action
There’s a frequent emphasis amongst Search engine marketing bloggers who focus on biotech & scientific industries on taking a top-down, topical takeover method to content material planning.
I got here throughout these posts after finishing this aggressive evaluation for our consumer. This topic-takeover emphasis was validating as a result of the “Findings-To-Motion” part of our examine prescribed one thing related:
Map matters to the funnel. Previous to key phrase analysis, map broad matters & subtopics to their respective locations within the informational & shopper funnel. Inside every subject vertical, establish:
- Questions-to-ask & problems-to-solve at every funnel stage
- Key phrase alternatives that roll as much as these respective phases
- What number of pages must be deliberate to rank for these key phrases
- The web site templates that greatest accommodate this content material
- The header & inner linking technique between these pages
Not like extra common-language industries, the necessity to enchantment to 2 audiences is very pronounced in scientific industries. One is the AI-driven viewers of search engine bots that scour this advanced semantic terrain for symmetry of clues and which means. The opposite is human, after all, however with a thoughts that has already mastered this symmetry and is extremely able to discerning it.
To take advantage of environment friendly use of time and person expertise, content material planning and supply must be extremely organized. The age-old advertising and marketing funnel idea works particularly effectively as an organizing mannequin. The remaining is the rigor of making use of this full-topic-coverage, content material method.
Zach Wales is Sr. Search engine marketing Strategist at Brainlabs.
Subscribe to the Search Engine Watch e-newsletter for insights on Search engine marketing, the search panorama, search advertising and marketing, digital advertising and marketing, management, podcasts, and extra.
Be a part of the dialog with us on LinkedIn and Twitter.



