Studying Time: 10 minutes
Actual-time streaming serves because the spine of the MoEngage product options. Proper from the early days of 2015-16, we’ve extensively used Apache Kafka and Apache Samza for real-time occasions processing for each stateless and stateful information pipelines.
Over the interval of the final 8 years, we’ve seen each the evolution of our personal product and a multifold improve within the scale of knowledge processing wants.
There have been a number of learnings with operating and working a big set of Kafka clusters together with Samza functions. Now we have carried out many upgrades and restructures to realize the perfect performances from these methods for our use instances.
Earlier, we revealed our studying of managing large Kafka clusters Kafka Redesign and Classes Discovered. Presently, we’ve a number of information facilities throughout geographies in AWS and Azure. We function with greater than 10 clusters in every information heart.
On this publish, we’re writing about how we’ve been bettering and additional restructuring one of many largest Kafka clusters.
State of Kafka Clusters
Now we have devoted Kafka clusters for varied enterprise use instances primarily based on our product options and consumer necessities.
This cluster handles site visitors of some million occasions per minute. There are a number of business-critical jobs which might be deployed as Samza functions. For these functions, streaming pipelines are anticipated to work with a Service Stage Settlement (SLA) in single-digit seconds for end-to-end processing.
An instance use case for this sort of strict SLA is time-critical actions/notifications despatched to clients every time they undergo a journey on an E-commerce web site. One other instance could possibly be sending a transactional OTP after the shopper accesses a security-enabled characteristic on the consumer web site/cellular app for identification re-verification.
The Want for Restructuring Kafka Clusters
Based mostly on strict SLAs at our information quantity, we would have liked to enhance our Kafka infrastructure. One of many largest Kafka clusters we function is ‘Kafka-automation’. We observe the nomenclature of naming Kafka clusters primarily based on the area. We lately restructured this cluster for higher efficiency. This internally serves a number of microservices and streaming jobs required to help this use case.
As talked about, our streaming information pipeline consists of Kafka and Samza stack for processing and clever ETL of event-based information. This stack has some inherent limitations, which received aggravated because the variety of jobs and site visitors on every job elevated over time.
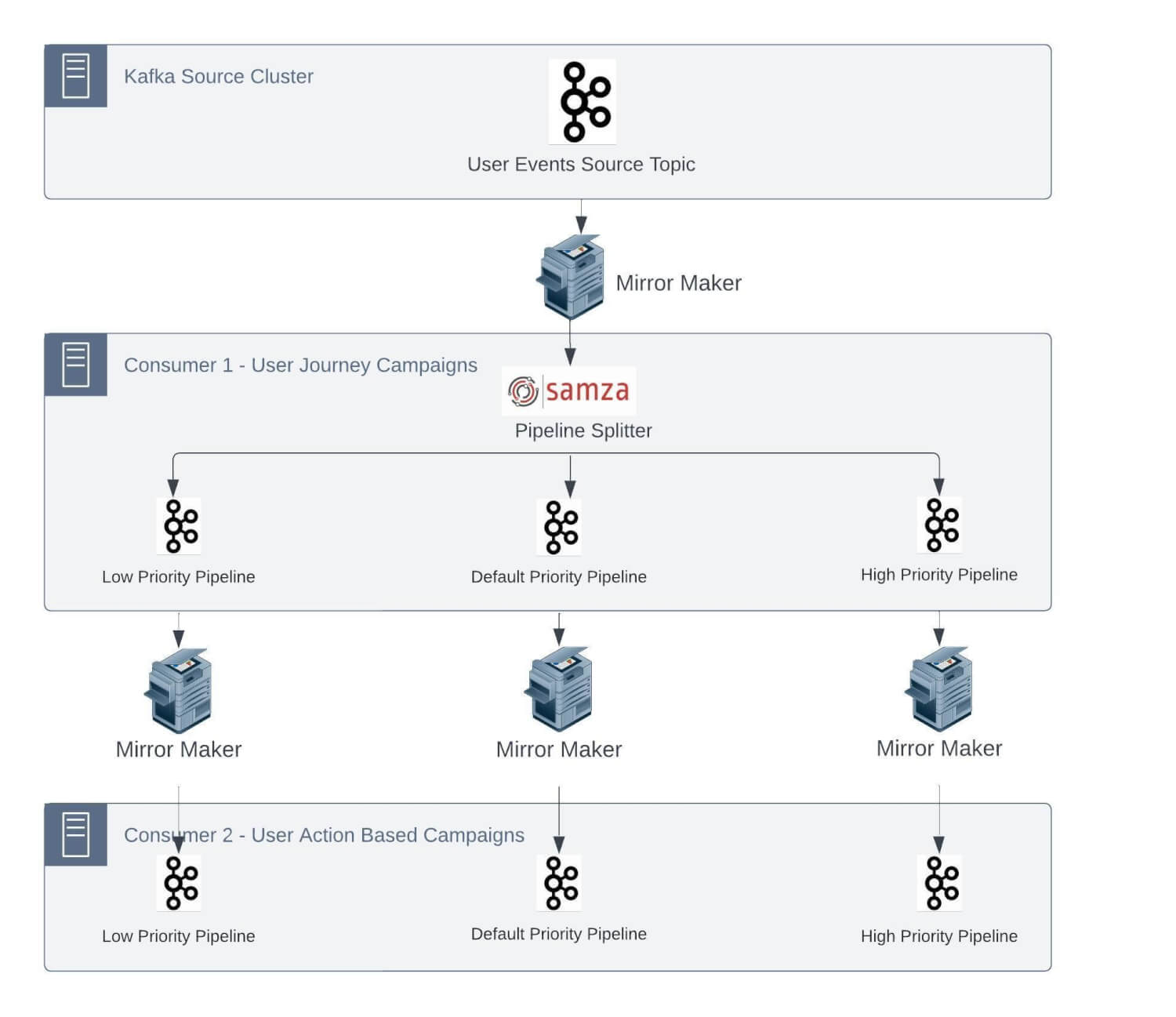
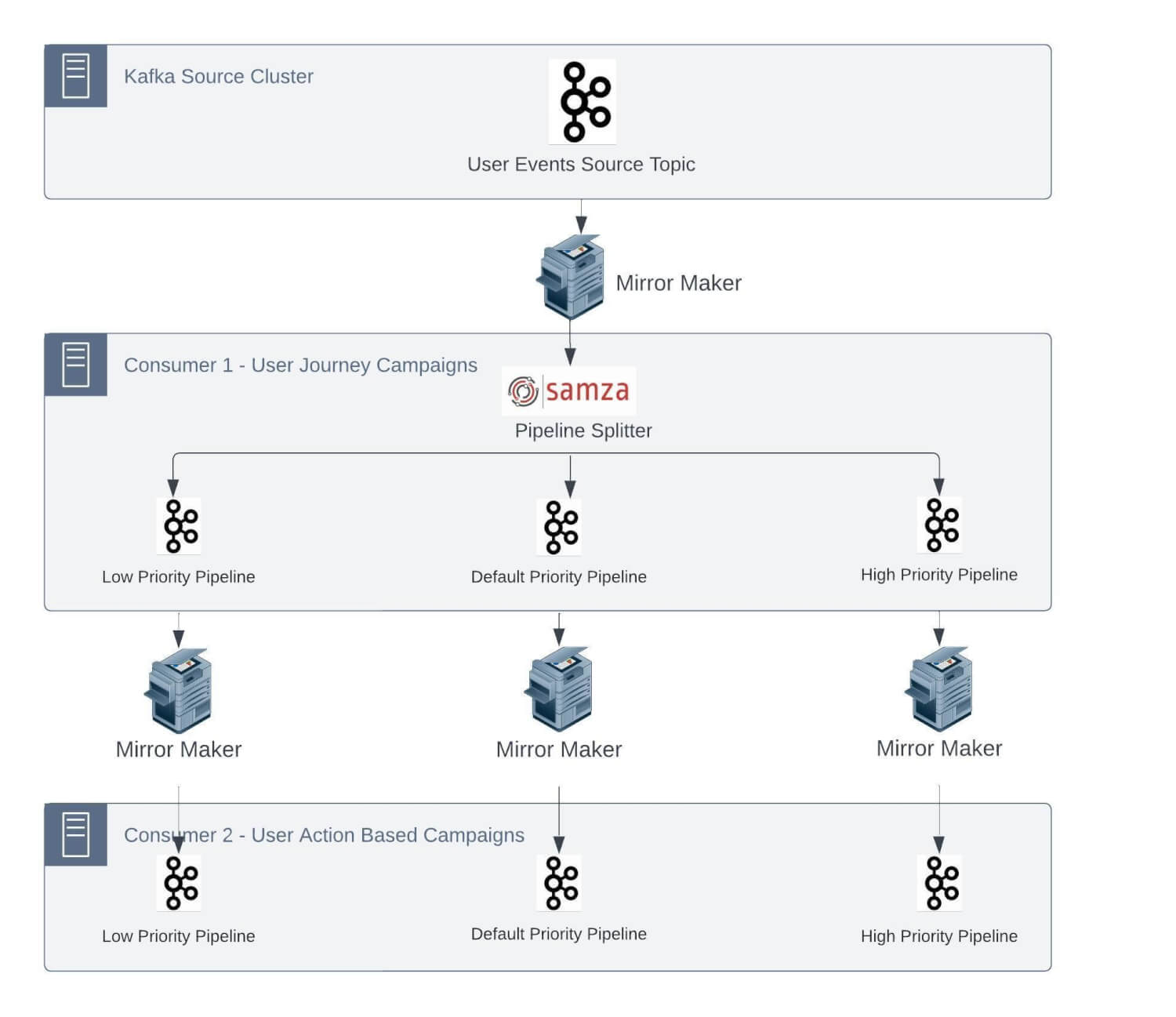
As most of those jobs have plenty of legacy code to allow the characteristic set and preserve SLAs, it’s not possible to thoroughly change this structure. We’ll now go deeper into among the vital challenges we have been dealing with:
1. One-to-one mapping of supply subject partitions with the variety of Samza containers
As talked about earlier, we’ve a number of stateful jobs. These Samza jobs have the inner state as changelog subjects within the Kafka cluster. Being a stateful software, a problem will come up to course of the occasion in an outlined SLA within the case of a changelog subject that doesn’t have the required state and must make a community name to a Database to retrieve the state.
We run Samza on yarn, and every container processes the occasions from a single partition of the Kafka subject to maintain the end-to-end processing time as little as doable. Samza course of and window capabilities observe single-thread semantics.
Now, let’s take a situation: assume that the typical time spent processing a message in stateful functions is 5 ms. Based mostly on this, the utmost throughput from a partition may be 200 messages per second. So, if we’ve to course of 100K msg/sec, it will require 500 partitions within the supply subject.
Contemplating our development charge and to deal with the height situations, we repartitioned this specific subject with 600 partitions within the Kafka cluster.
We use Rocksdb because the native cache for Samza StreamTask. This reduces the necessity to fetch information from any exterior supply at processing time and retains on getting up to date by database CDC Kafka subjects. The way in which Samza operates, we have to have the related cache for occasion processing routed to the right yarn container in order that no community name is required.
This requires messages in several subjects to be produced with the identical key/identifier such that they all the time go into the identical partition quantity and forces these enter streams to have the identical variety of partitions.
So now, different ingestion CDC subjects required to replenish the Rocksdb cache should even be created with the identical variety of partitions.
These jobs can have a number of inside states, too. For instance, if an software has 4 inside states and would have corresponding 4 changelogs, which get created with the identical variety of partitions by the Samza software.
Particular to this use case thus far, we’ve 1 Unified subject, 2 CDC subjects, 4 changelog subjects, and seven subjects, every with 600 partitions. As time handed, we onboarded extra Samza functions, consuming occasions from the unified stream. We additionally had low-, medium-, and high-priority subject separations, leading to much more subjects within the Kafka cluster.
This has been an operational nightmare for us, forcing upstream groups to repartition and rebalance subjects primarily based on downstream jobs to work correctly.
2. Deserted/Unused changelog subjects
Samza creates changelog subjects primarily based on its software ID. Generally, software IDs should be modified resulting from model updates or inside job constraints. This ends in present changelog subjects being deserted and recreating new changelog subjects for brand spanking new software IDs. Some jobs require frequent software ID modifications resulting from their nature of requirement.
By default, these changelog subjects are created as log compact subjects. Therefore, they preserve keyed messages in subjects even when these subjects are deserted and won’t be utilized in Sazma functions.
3. Brokers efficiency degradation
We began dealing with some important points with the brokers as site visitors grew over time. 1-to-1 mapping forces even subjects with smaller use instances with a low message charge to be created with 600 partitions.
We reached a stage the place our Kafka cluster with 8 brokers was operating with greater than 20K+ partitions on every dealer and 100K+ partitions in whole, together with replicated partitions.
This induced efficiency degradation for our brokers. We began dealing with the challenges mentioned beneath usually.
- Too many open recordsdata errors: Every partition on the dealer has a logs listing within the file system the place it shops the messages. For each partition, brokers maintain two recordsdata (one for the index and one other for appending the precise message information) opened per log section. There was greater than 300K+ recordsdata opened on every dealer. Per our earlier Kafka expertise of operating Kafka clusters, all of the brokers have been initially configured with 100K file descriptor limits. As subjects grew, the variety of file descriptors required began breaching the max restrict, and we began receiving errors for brokers being both down or restarted resulting from too many open file errors.
- Points with compaction subjects – Earlier than we dive deeper, take a look at Kafka compaction if you’re not conscious of the working dynamics of log compaction retention coverage in these posts – An investigation into Kafka Log Compaction and https://towardsdatascience.com/log-compacted-topics-in-apache-kafka-b1aa1e4665a7. Let’s perceive among the key configurations utilized in log compaction and the way they impacted our brokers –
-
-
section.ms– This configuration controls the time frame after which Kafka will drive the log to roll even when the section file isn’t full to make sure that retention can delete or compact previous information and the default worth is 7 days. So if there are very low message in-rates, log segments are closed after days, and publish that, deletion or compaction is carried out. -
min.washer-friendly.soiled.ratio– This configuration controls how regularly the log compactor will try to wash the log (assuming log compaction is enabled). By default, we are going to keep away from cleansing a log the place greater than 50% of the log has been compacted. If there are very low in-rates in subjects, then compaction is triggered in longer intervals, and if subjects haven’t any new incoming messages, Then compaction won’t be triggered in any respect, and messages/logs-segment will retain the desk area perpetually. -
cleanup.coverage=compact,deleteforms of functions, you could have home windows of time with many variations of the important thing. In the course of the window, you solely need to retain the newest model of the important thing. Nonetheless, as soon as the window has expired, you want to have the segments for the window deleted. With each compact and delete-enabledretention.msof the changelog can be set to a price larger than the retention of the window. Though previous home windows received’t robotically be eliminated on expiration, the dealer will ultimately take away them because the previous segments expire. -
cleanup coverage–compact -> deleteSome changelog subjects merely work a caching the place the state may be constructed by querying the database.
-
-
Excessive CPU utilization – With our expertise of operating a Kafka cluster, we’ve realized that there’s a direct relation between ProduceRequests and Latency. Increased ProduceRequests result in larger CPU utilization on brokers and elevated latency. To maintain our cluster steady, we anticipated decreasing ProduceRequest counts as a lot as doable. It may be assumed {that a} Kafka producer will generate extra ProduceRequests if a subject has extra partitions. Since we created subjects with 600 partitions and added extra subjects, we reached a stage the place Kafka brokers all the time had ~90% CPU utilization.
-
Excessive disk utilization alerts – Many subjects had retention of weeks and month(s). A whole lot of excessive disk utilization alerts have been induced resulting from such subjects.
Attributable to these issues, we’ve been bombarded by Pager Responsibility alerts one after the opposite, which has induced degradation within the high quality of service we need to preserve. We nonetheless handle the margin of security with extra infra so we don’t breach any client-side SLAs. This extra margin of security has inflated the infrastructure value for the clusters.
Additional, scaling and pushing new options has been troublesome resulting from these points. Each time a brand new characteristic was deliberate for launch, we would have liked to do a viability research on our present infrastructure and plan in response to that. This has elevated the launch time for a few our merchandise.
Multi-pronged Options For Main Points
With operating a cluster with all of the above challenges, we realized that creating subjects with many partitions doesn’t bode properly for upkeep and smoother operations.
We applied among the options listed beneath to deal with the foremost challenges detailed within the above part:
-
We can’t get out of Samza instantly. Attributable to this, we can’t utterly resolve 1 to 1 mapping of subject partitions to Samza job containers. We determined to cut back the variety of partitions and containers on the Samza aspect and improve the processing capability of particular person containers to accommodate for the processing velocity. We revisited Samza software configurations reminiscent of producer batch measurement, linger ms, compression kind subject replication issue, and so forth. to cut back the end-to-end processing time.
We additionally segregated stateless and stateful jobs in order that we may have a simple scaling course of.
-
As talked about earlier, when the applying ID for a Samza job is modified, a brand new set of changelog subjects is created, and older modified subjects are merely deserted.
We sometimes see plenty of changelog subjects leading to enormous numbers of opened recordsdata, numbers of partitions on brokers, and the dealer because the chief for partitions.
Our method for cleansing these subjects was easy: we listed all of the subjects that didn’t obtain any site visitors within the final week and thought of them as deserted/unused. We modified the cleanup coverage to delete and decreased retention to 1 minute.
With these modifications, messages have been cleaned from disks, however to cut back the opened file counts, we additionally needed to eliminate these partitions-metadata from the disk too. Since we’ve subject deletion disabled for our enterprise requirement, it’s not possible to allow subject deletion quickly by altering the dealer’s configuration and deleting them because it requires dealer restarts. So, we’ve added a dummy dealer occasion within the cluster and moved all such deserted subjects to this dealer by decreasing the replication issue to 1. With these modifications, we’ve cleaned up the disk area and decreased opened recordsdata from brokers considerably.
Nonetheless, a brand new problem arose when a brand new subject creation may have partitions on this dummy dealer. So we had to decide on which brokers to make use of for partition distribution to keep away from dummy brokers.
-
We additionally elevated our dealer’s file descriptor limits to cut back too many open file errors. This gave non permanent aid to the on-call staff.
-
We tuned our dealer’s configuration to our latest wants. We decreased the section.ms to 1 day for quicker deletion and early compaction triggers. We modified min.washer-friendly.soiled.ratio = 0.1 to allow an aggressive compaction technique. This decreased the disk area utilization and opened file depend. Some subjects have very giant stateful states. We began enabling each insurance policies and set cleanup.coverage=compact, delete for log compaction subjects to cut back disk area utilization additional. We additionally modified the cleanup coverage from compact to delete wherever we may stay with the roles fetching information from sources like databases and never Kafka subjects on restarts. This additional decreased disk utilization.
-
To lower the latency and cut back dealer CPU utilization, we experimented each with horizontal and vertical scaling and located a threshold {that a} dealer can serve inside the desired SLA if the ProduceRequests depend stays inside a restrict and located it to be roughly 4K for our use instances. However we would have liked so as to add extra jobs and subjects shortly so horizontal scaling (including extra brokers) grew to become the first possibility.
Once more, horizontal scaling requires manually redistributing the partitions to newly added brokers. Excessive-volume subjects required extra time to steadiness. Redistributing high-volume subjects additionally decreased disk utilization on older brokers and elevated utilization on newer brokers.
-
We requested our groups to re-access retention for his or her respective jobs and convey it to the minimal doable interval with out inflicting SLA breaches.
With all of the above options and sustaining normal practices in thoughts, we created two new Kafka clusters for stateful and stateless jobs. All the subject partitions have been reevaluated or recreated with fewer partitions and the fitting replication elements wherever doable. Publish-migration, Now we have seen an enormous enchancment in latency and SLA adherence.
NOTE: Not detailed, however we nonetheless have a few of these challenges due to enterprise constraints, which aren’t a part of this publish.
-
We’re additionally creating subjects with larger partition counts for low-in-rate subjects.
-
We nonetheless see the applying being modified for Samza jobs and deserted subjects on brokers.
-
A couple of subjects stay the place retention is of weeks and months.
-
Samza jobs nonetheless require additional tuning, reminiscent of batch measurement, linger ms, compression, and so forth.
Conclusion
Every time there’s an ask for SLA enchancment or latency discount, we should always relook at bettering software code, community calls, and caching and reevaluating the processing engine itself. Growing assets like partition depend and container counts, and so forth, ought to be evaluated with nice care.
With a greater understanding of Kafka utilization and Samza tuning, we have been in a position to enhance the reliability of our system. We will uphold our SLA dedication to our clients rather more than we did with our older cluster, and we will do it with a 40% value discount.
However many of those fixes are nonetheless not fixing the actual root explanation for issues. These have given us respiration area and allow us to serve the shoppers rapidly.
Most issues associated to throughput and latencies are born out of Samza’s occasion processing mannequin. Limitation in parallelizing the varied operators remains to be a bottleneck for us.
Now we have evaluated different streaming alternate options, and stream processing with Flink appears appropriate for fixing most of our challenges. We plan to maneuver out of Samza over time to implement a long-term answer for these challenges.
Altering the stack in a single go is inconceivable for a big group like MoEngage. Now we have internally launched Flink-based streaming PAAS for our new jobs. This implementation makes use of Kubernetes as an orchestrator. This will even assist transfer away from Yarn-based job deployments and convey service containers and streaming jobs on the identical orchestration layer. However will probably be some time earlier than we go away solely large Samza jobs. Till then, we are going to nonetheless have to take care of and function among the legacy implementations.
The publish Bettering Reliability by Restructuring Kafka Cluster on MoEngage appeared first on MoEngage.