30-second abstract:
- Bounce charge is the share of single-page visits or visits wherein the individual left your website from the doorway (touchdown) web page
- This metric helps measure go to high quality and relevance
- Exit charge is a metric that identifies the variety of exits out of your website, and, as with entrances, it’s going to at all times be equal to the variety of visits when utilized over your total web site
- Use this metric together with explicit content material pages with a purpose to decide the variety of occasions that individual web page was the final one seen by guests
- Pages that fail to satisfy customer expectations, don’t present clear navigation, discuss options fairly than advantages, and content material that’s not actionable all enhance bounce charge
Google Analytics supplies precious intelligence into how guests discover, work together with and depart your web site. This intelligence is central to bettering each consumer expertise and the profitability of your web site. Google Analytics supplies many helpful metrics that assist you do that and two of probably the most helpful are the bounce charge and exit charge.
The distinction between a bounce and an exit might be complicated, particularly in case you are new to analytics. The aim of this text, then, is to demystify the 2 and clarify why they’re essential. It additionally acts as a information to deciphering bounce and exit knowledge and how you can decrease them with a purpose to enhance the efficiency of your web site and enhance conversions.
Making an entrance that counts
Earlier than you’ll be able to perceive and calculate bounce charge you might want to know a bit about entrance pages, additionally known as touchdown pages and entry pages. Google defines an entrance web page as:
Entrances
This metric identifies the variety of entrances to your website. It would at all times be equal to the variety of visits when utilized over your total web site. Thus, this metric is most helpful when mixed with explicit content material pages, at which level, it’s going to point out the variety of occasions a specific web page served as an entrance to your website.
In brief, an entrance web page is the primary web page a customer lands on when visiting an internet site. Entrances are, as we’ll see, a key consider calculating bounce charge.
Tips on how to view your entrances?
In Google Analytics, you’ll be able to simply view your entrances by following these easy steps:
- Go to “Conduct,” underneath “Stories”
- Click on on “Web site Content material”
- Click on on “All Pages”
- View your “Entrances”
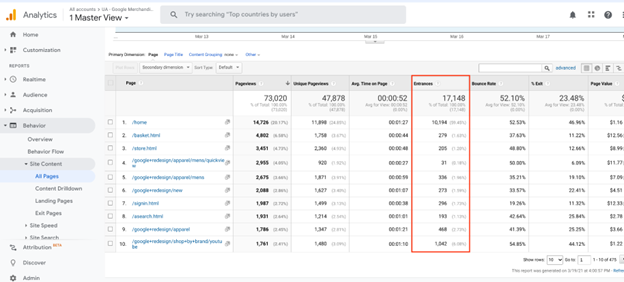
Entrances are significantly useful since they’ll present you which of them pages are bringing probably the most visits to your website. They’ll additionally let you know the alternative and assist you establish the weakest pages with decrease bounce charges.
Nicely, what’s a bounce?
A bounce is a single-page go to. A bounce happens when a customer enters and exits an internet site viewing no different pages aside from the doorway web page.
And, what’s bounce charge?
If, for instance, 100 guests enter your website through Web page “A” and 20 of them depart with out clicking by to some other web page, web page “A” would have a bounce charge of 20 %.
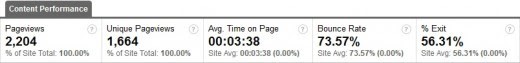
The above determine exhibits site-wide averages.
A number of the experiences Google Analytics generates will give site-wide averages. The display screen seize above has been taken from the ‘Prime Content material’ report which might be discovered by clicking the Content material tab in your Google Analytics dashboard.
The very first thing you would possibly discover is that once you add the common bounce charge and the common exit charge collectively the result’s higher than one hundred pc. If bounce charge and exit charge are measures of how many individuals depart your website, how can the whole be higher than one hundred pc. The reply is that it may’t.
You is perhaps fooled into considering that bounce charge is calculated as a proportion of Pageviews. It is a logical thought since it’s figured within the report. Nevertheless, when added collectively, bounces and exits would once more be higher than the whole Pageviews.
Bounce charge will not be primarily based on the variety of guests or the variety of web page views it’s primarily based on entrances.
Why do individuals bounce?
Individuals bounce due to many causes the important thing to lowering your bounce charges lies in figuring out and addressing the commonest ones:
1. When pages don’t meet expectations
Let’s say, for instance, that you’re searching for a brand new air fryer. So that you Google “purchase air fryers free transport”. You see an advert that claims “air fryers With Free Transport”. So that you click on on it. However once you click on on the advert, as a substitute of a touchdown web page about completely different air fryers, you’re on the positioning’s homepage. What are you going to do? Bounce again to Google and make a brand new analysis to discover a web page that’s 100% about air fryers.
2. When design is ugly
Having an unpleasant design also can lead customers to bounce again. Individuals largely decide web sites first, primarily based on design, and second on the content material.
3. When the web page offers customers what they’re searching for
Sure. Not all bounces are “dangerous”. A bounce might be, the truth is, an indication that your web page gave customers precisely what they have been searching for.
For instance, I’ve been trying personally over the previous few days for a low-carb hen soup recipe and I landed on this recipe web page. This touchdown web page had every part I wanted to make the recipe: components, detailed directions, and photos. So, as quickly as I obtained my soup to simmer over medium-low warmth, I closed the web page.
Even if this single-page session is “technically” a bounce, it isn’t as a result of that web site suffered a nasty UX or an unpleasant design. It’s simply because I obtained what I wanted.
Figuring out pages with excessive bounce charges
Discover the determine under that exhibits sitewide entrances and bounces.

To get at the actual numbers that contribute to bounce charge you might want to dig a bit deeper. The display screen seize above has been taken from the ‘Prime Touchdown Pages’ report which can be discovered by clicking the Content material tab in your Google Analytics dashboard.
As you’re employed your approach down the report you can even view bounce charges for particular person pages.
![]()
The above determine exhibits the bounce charge at a web page degree.
The ‘Prime Touchdown Pages’ report helps establish pages with excessive bounce charges that may require additional investigation.
You possibly can clearly see from Determine three how the bounce charge is calculated for a single web page: (283 bounces / 303 entrances) * 100 = 93.39939939934% which analytics has rounded as much as 93.40%. As fascinating as that is, it tells us nothing about what’s driving the bounce charge and what steps to take if any are required to decrease it.
Bounce charge by poor consumer expertise
Pages that fail to satisfy customer expectations, don’t present clear navigation, discuss options fairly than advantages, and present content material that’s not actionable – all enhance bounce charge. Not all guests in your website are utilizing desktop machines with ultra-fast connections and can abandon your website if a web page takes too lengthy to obtain. When you have been over-zealously linking to your website, hyperlinks from pages that aren’t carefully associated also can enhance the bounce charge. These are all issues you’ll be able to take a look at for and repair to a level.
Lacking timestamps and the pages time forgot
Google Analytics experiences the time guests spend on pages by evaluating timestamps. When a customer lands on a web page a timestamp is created which data the exact time they arrived.
If a customer arrives at web page “A” at 13.45 and clicks by and lands on web page “B” at 13.47 two timestamps will likely be created. By subtracting the time the customer lands on web page “A” from the time they land on web page “B” you arrive on the time spent on web page “A”:
13.47 – 13.45 = 2 minutes spent on web page “A”.
If at 13.50 the customer leaves your website utterly no timestamp is created and there’s no method to inform how lengthy the customer spent on web page “B”.
Why was no timestamp created? If the web page was outdoors the scope of your analytics account, on one other area for instance, the timestamp can’t be accessed by your analytics account. Subsequently, the time spent on that web page can’t be decided for that web page view.
Equally, the time spent on a web page by customer who enters a website and bounces with out visiting some other web page can’t be measured both.
Cookies, periods, and timeouts
Google Analytics makes use of cookies to trace the exercise of holiday makers to your pages and report these actions again to their server. Cookies allow Google to differentiate the actions of every customer individually and monitor sequential web page visits made by the identical consumer throughout their time (session) in your web site. This info is then reported again to you once you log into your Google Analytics account.
Each bounce or exit is the results of a session timeout. In Google Analytics, a session will timeout after half-hour of browser inactivity. If a customer navigates to a different web site, the session will nonetheless proceed for a most of half-hour earlier than registering a bounce or exit. So long as the customer returns earlier than the session occasions out and clicks by to a different web page of your web site, it is not going to be thought of as both a bounce or an exit.
- Every go to to your website culminates in a session timeout
- A session that occasions out after a single web page view is classed as a bounce
- A session that occasions out after a number of web page views are classed as an exit
Take a look on the tabs open in your browser proper now – what number of have been open for greater than 29 minutes with none exercise? Regardless of the web page nonetheless staying open in your browser, a number of the periods related to particular person pages may need already timed out inflicting an exit or a bounce. Additionally closing your browser, disconnecting from the web, or hitting the again button will all trigger a session to trip which can seemingly be recorded as a bounce or an exit in somebody’s Analytics.
Subscribe to the Search Engine Watch publication for insights on website positioning, the search panorama, search advertising, digital advertising, management, podcasts, and extra.
Be part of the dialog with us on LinkedIn and Twitter.

