Excel can do extra than simply basic math. That is because of its bevy of built-in features and min-formulas that simplify the creation of extra advanced formulation.

In my decade-long expertise with Excel, I’ve discovered that one of many extra helpful features is the COUNTIF operate.
You should use COUNTIF to rely the variety of cells that comprise a particular worth or vary of values. It’s simpler to make use of COUNTIF than to manually rely your self.
Methods to Use the COUNTIF Perform in Excel
The COUNTIF operate in Excel counts the variety of cells in a spread that meet the given standards. It doesn’t complete the cells; it merely counts them. I’ve discovered it helpful for counting cells that comprise a particular worth or vary of values.
For instance, let’s say you could have a spreadsheet that accommodates buyer contact info, together with road addresses and ZIP codes. You’ll be able to simply use the COUNTIF operate to rely what number of prospects stay in a given ZIP code — and also you don’t even should type the addresses by ZIP code to do it.
Let’s work by the method step-by-step.
1. =COUNTIF()
Start by coming into the next into the cell the place you wish to place the reply:
=COUNTIF()
For this instance, we’ll use a grocery listing that I’ve written. The totally different gadgets I wish to purchase are sorted by kind, like greens and fruit.
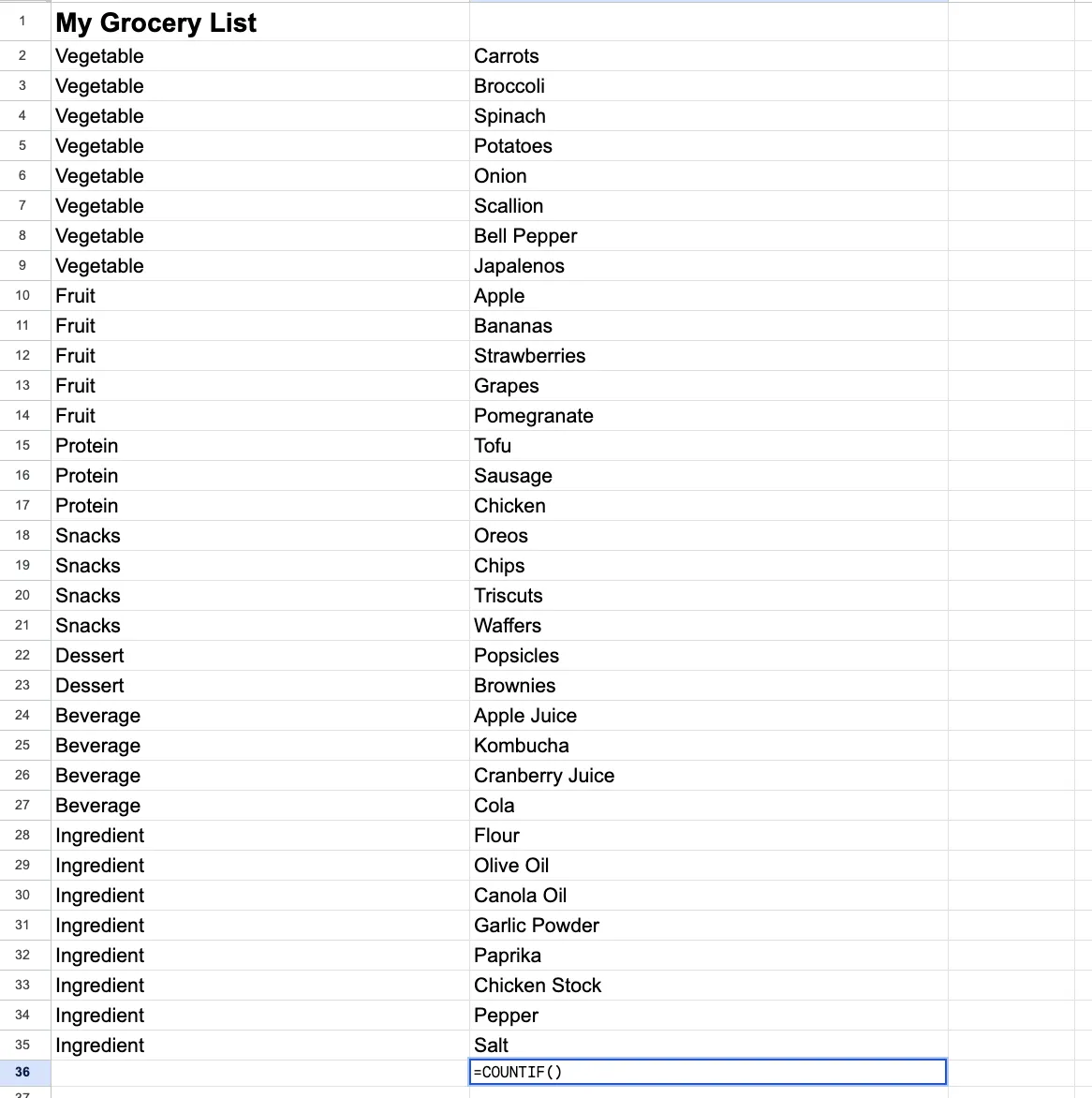
2. Outline a spread of cells.
For the COUNTIF operate to work, you need to enter two arguments between the parentheses — the vary of cells you’re and the standards you wish to match.
Place your cursor throughout the parentheses and both manually enter the vary of cells (e.g., D1:D20) or use your mouse to focus on the vary of cells in your spreadsheet.
Assuming your ZIP code values are in column D from row 1 to row 20, the operate ought to now appear like this:
=COUNTIF(A2:A35)
3. Add a comma.
Subsequent, kind a comma after the vary, like this:
=COUNTIF(A2:A35,)
4. Outline your search standards.
You now have to enter the factors or worth that you just wish to rely after the comma, surrounded by citation marks.
In our instance, let’s say you’re trying to see what number of greens are in your listing. On this occasion, the factors you’re counting is Vegetable, and your operate ought to now appear like this:
=COUNTIF(A2:A35, “Vegetable“)
Be aware that your standards could be a quantity (“10”), textual content (“Los Angeles”), or one other cell (C3). Nonetheless, for those who reference one other cell, you don’t encompass it with citation marks. Standards are usually not case-sensitive, so you possibly can enter “Pink,” “purple,” or “RED” and get the identical outcomes.
5. Activate the operate.
Press Enter, and the operate prompts, returning the variety of cells that match your argument.
Ideas for Utilizing the COUNTIF Perform
Many customers, myself included, have found that you should use the COUNTIF operate in many various methods apart from counting particular values. Listed here are three ideas I like to recommend for extending using the COUNTIF operate.
Use wildcard characters for partial matches.
You don’t should reference a particular worth or standards. For those who solely know a part of the worth you wish to rely, you should use the * wildcard character to match any worth in that a part of the worth.
For instance, let’s say you could have a listing of addresses. If you wish to match all ZIP codes that begin with the numbers 46 (akin to 46032, 46033, and 46450), you’d enter 46 adopted by the * wildcard, like this:
=COUNTIF(D1:D20,“46*“)
You should use the wildcard character at both the start or the tip of the worth string. For instance, to rely all cells that finish with the letters “polis,” enter the next:
=COUNTIF(D1:D20,“*polis“)
This can rely cells that comprise the cities of Indianapolis and Minneapolis.
Rely values which might be higher than or lower than a quantity.
For those who’re working with numbers, you might wish to rely cells with values higher than or lower than a given worth. You do that through the use of the mathematical higher than (>) and fewer than (<) indicators.
To rely all cells which have a price higher than a given quantity, akin to 10, enter this:
=COUNTIF(D1:D20,“>10“)
To rely cells which might be higher than or equal to a quantity, enter this:
=COUNTIF(D!:D20“>=10“)
To rely all cells which have a price lower than a given quantity, enter this:
=COUNTIF(D1:D20“<10“)
To rely cells which have a price lower than or equal to a given quantity, enter this:
=COUNTIF(D1:D20“<=10“)
You’ll be able to even rely cells with a price not equal to a particular quantity. For instance, to rely cells that aren’t equal to the quantity 10, enter this:
=COUNTIF(D1:D20“<>10“)
In all these situations, keep in mind that the factors, together with the lower than, higher than, and equal indicators, have to be enclosed inside citation marks.
Rely one worth OR one other.
The COUNTIF operate may also be used to rely a number of standards—that’s, cells that comprise one worth or one other.
For instance, you may wish to rely prospects who stay in both Los Angeles or San Diego. You do that through the use of two COUNTIF features with a + between them, like this:
=COUNTIF(D1:D20,“Los Angeles“)+COUNTIF(D1:D20,“San Diego“)
So as to add much more values, enter one other + and COUNTIF operate.
If you wish to get much more out of Excel, try our article on easy methods to use Excel like a professional. You’ll discover 29 highly effective ideas, methods, and shortcuts that can make Excel even simpler to make use of.
Getting Began
For those who’re trying to rely the variety of gadgets that match particular standards, the COUNTIF operate is the way in which to go. You could possibly simply type on that column and manually rely the entries, however utilizing COUNTIF is an entire lot simpler.
Now, strive it out and save your self a while.

![Download 10 Excel Templates for Marketers [Free Kit]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/9ff7a4fe-5293-496c-acca-566bc6e73f42.png)
