Profitability is a key measure of an organization’s success, particularly for startups. Traders need to know if an organization’s core actions may end up in a revenue, so that you’ll have to know and perceive your organization’s working earnings.

Roughly 20% of small companies fail of their first 12 months of enterprise. Whereas turning into worthwhile in your first 12 months of enterprise is difficult, in case you are worthwhile, it is a optimistic indicator that your organization is on the right track.
However how can we calculate profitability? It isn’t as laborious as you may suppose. Discover out beneath.
What is working earnings?
Working earnings is a measure of an organization’s profitability. Principally, it’s the revenue left over after bills are taken away from a firm’s income. It is calculated by subtracting working bills from working income.
The ensuing quantity is proven as a subtotal on an organization’s multi-step earnings assertion. Working earnings is often known as working revenue, working earnings, or earnings from operations.
Collectors and traders take a cautious take a look at an organization’s working earnings. This quantity offers them a clearer image of the enterprise’ scalability or capability for future progress.
For instance, a optimistic working earnings reveals there’s room for the corporate to develop in its trade. In the meantime, a damaging working revenue might imply the enterprise is much less prone to scale up and develop.
Now that we’ve realized what working earnings is, let’s take a deeper look into the small print and be taught the steps to calculate your small business’ working earnings.
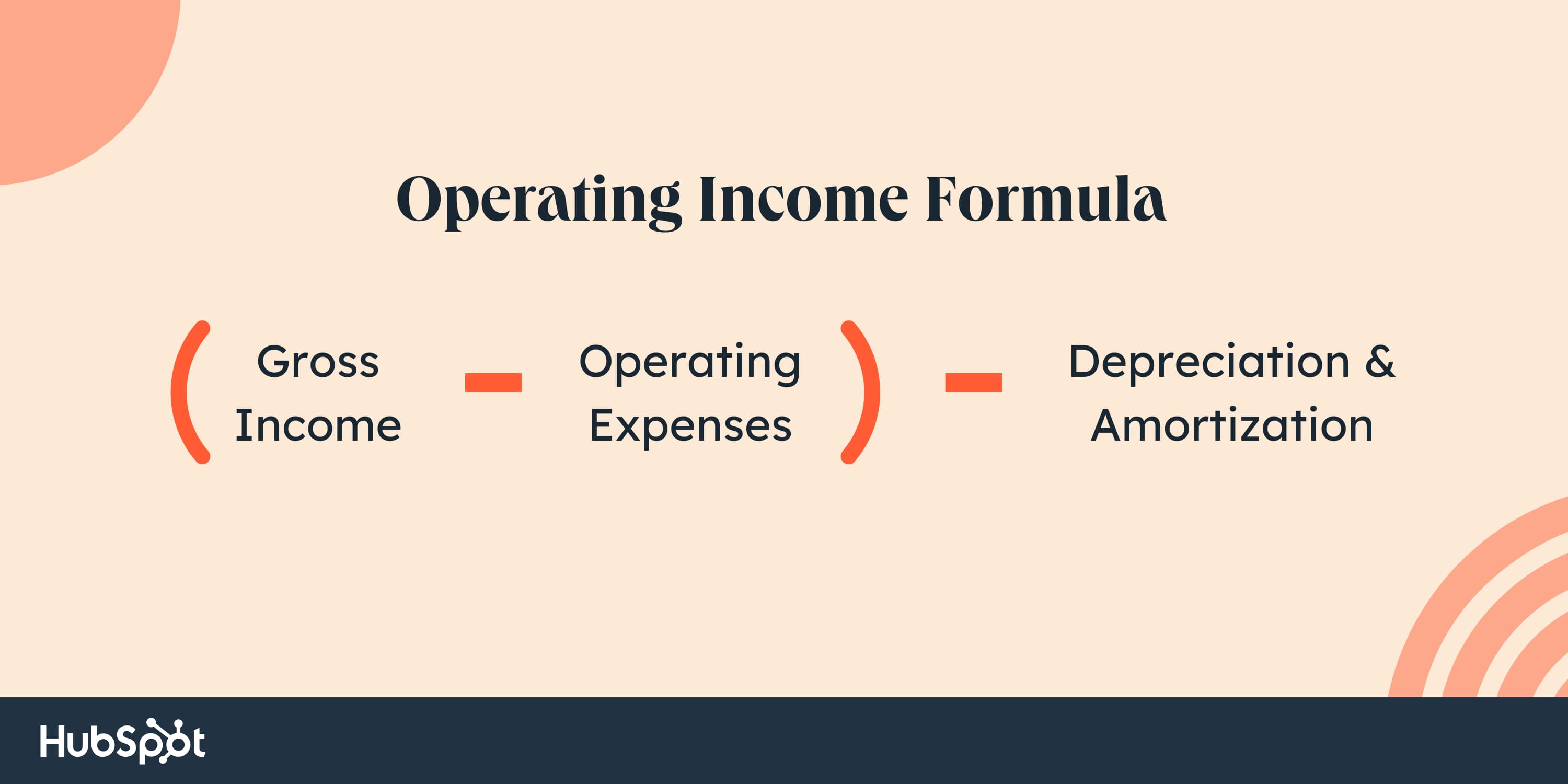
Working Revenue Method
- Begin with gross earnings.
- Subtract working bills.
- Subtract depreciation and amortization.
- The ensuing quantity is working earnings.
Let’s outline just a few key items of the working earnings method.
1. Gross Revenue
Gross earnings is the amount of cash your small business earns earlier than any taxes or different deductions are subtracted from it.
Lenders use this quantity as an indicator of how a lot cash you’re prone to borrow. They typically ensure you don’t borrow greater than your gross earnings complete.
2. Working Bills
That is the mixed complete of the prices of working your core enterprise actions. Widespread working bills embrace:
- Hire.
- Utilities.
- Price of provides.
- Wages.
- Gross sales commissions.
- Insurance coverage.
- Authorized charges.
- Price of products bought (COGS).
One key part of working bills is COGS. Beneath is the method for COGS:
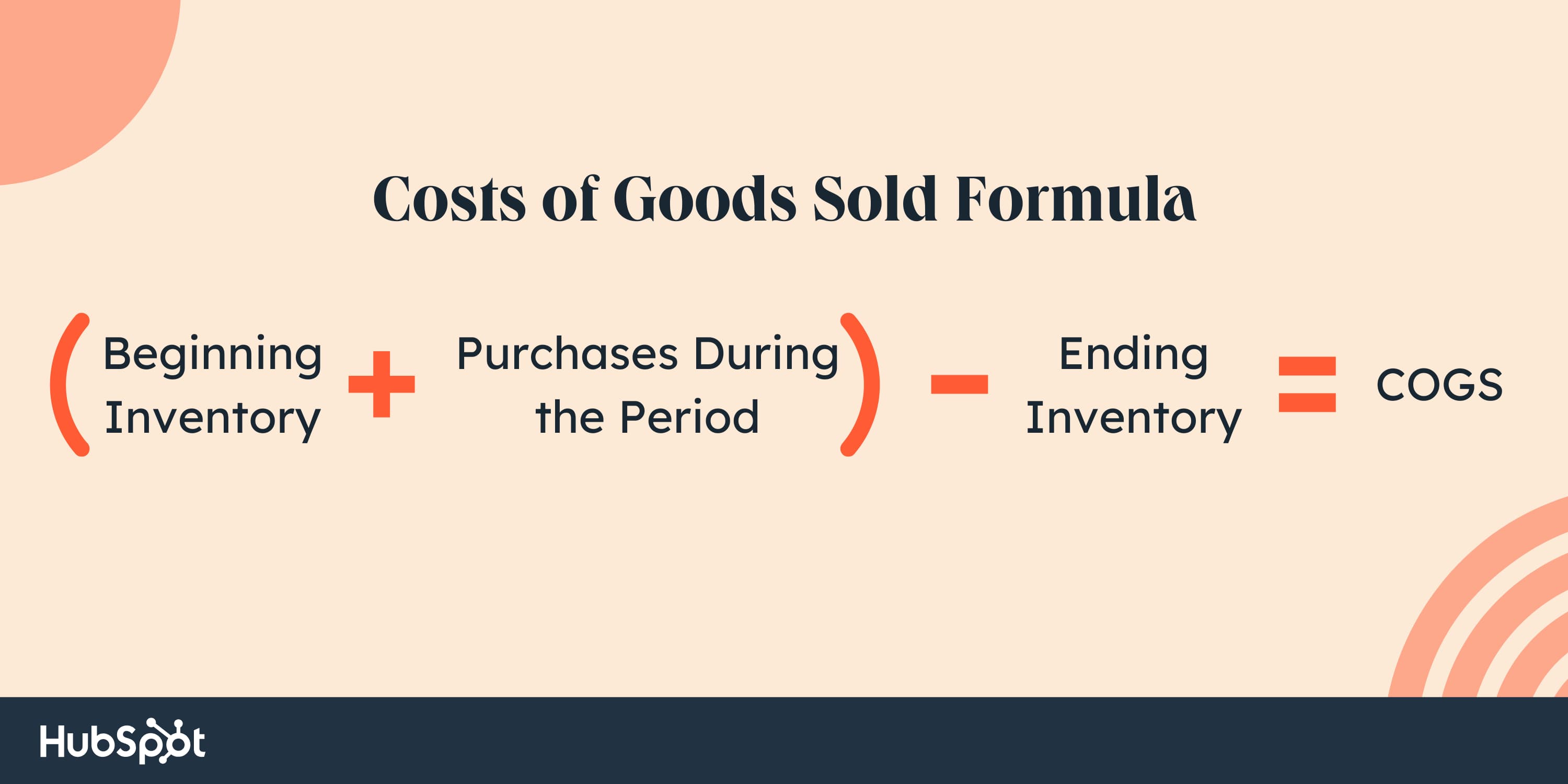
Starting stock is the merchandise that wasn’t bought within the earlier 12 months. Purchases through the interval embrace the price of producing extra merchandise or shopping for extra merchandise.
On the finish of the 12 months, the unsold merchandise (ending stock) are subtracted from the sum of the start stock and purchases through the interval.
3. Depreciation and Amortization
Depreciation and amortization are bills that account for the price of property over the lifetime of their use. These numbers are discovered within the working expense part of the earnings assertion and are reported through the interval of every asset’s use.
Depreciation includes expensing of tangible property over their helpful life. Tangible property, or fastened property, are bodily property corresponding to buildings, automobiles, gear, workplace furnishings, and so on.
Depreciation is calculated by subtracting the asset’s resale worth from its authentic value — and that is expensed over the course of the asset’s anticipated life.
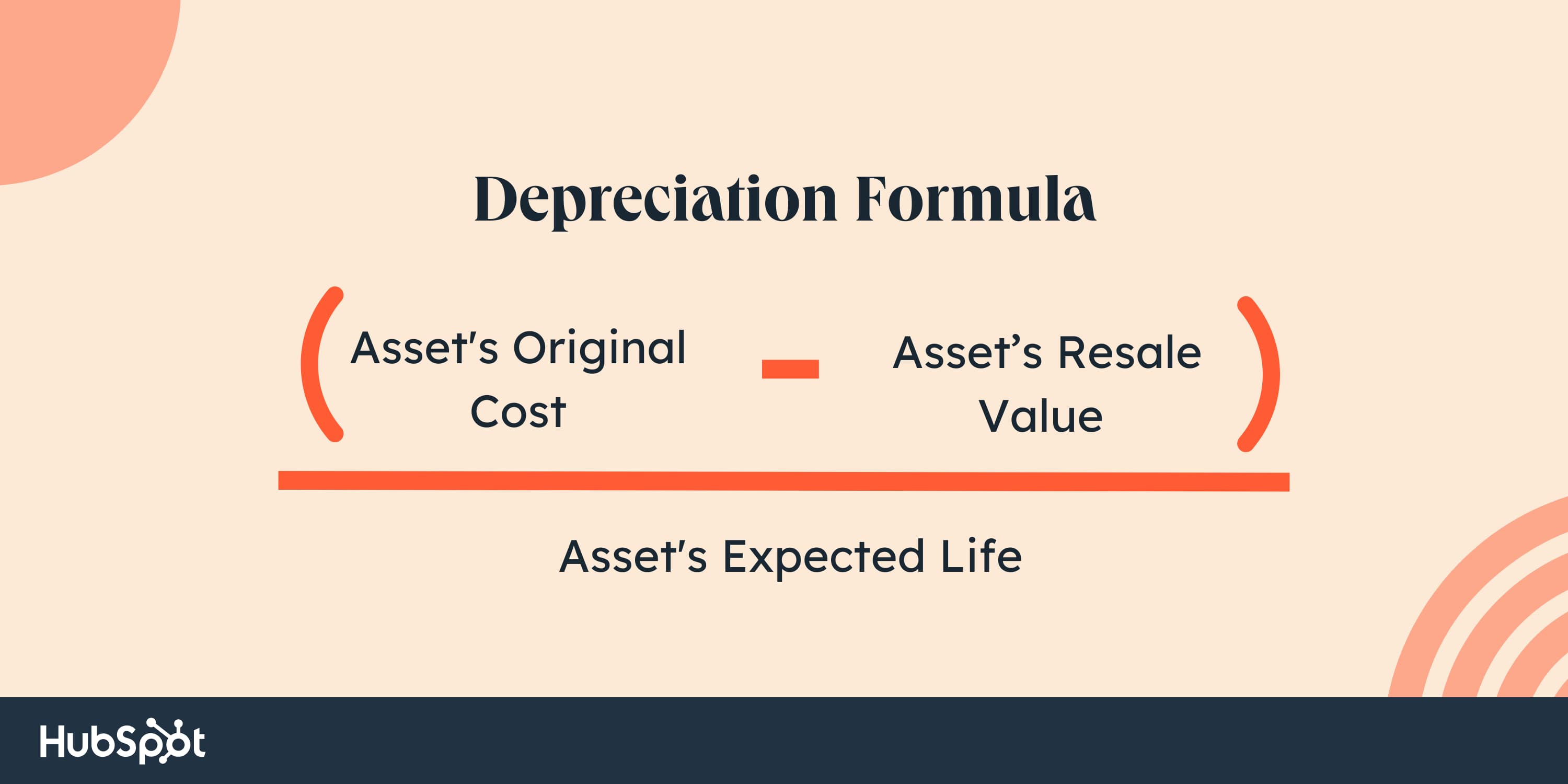
For instance, if a enterprise buys a machine that prices $10,000, the enterprise bills the fee over the machine’s 10-year lifespan. The resale worth after 10 years is $2,000. The depreciation calculation would appear like this:
($10,000 – $2,000) / 10 years = $800
The corporate will expense $800 every year till the machine is totally paid off within the tenth 12 months.
Amortization is much like depreciation, besides it includes expensing of intangible property.
Examples of intangible property embrace logos and patents, copyrights, franchise agreements, and so on. In contrast to tangible property, these intangible property usually don’t have any resale worth on the finish of their life.
Working Revenue Examples
Let’s take a look at just a few examples of working earnings.
Instance 1: Sarah’s Bakery
Sarah’s Bakery focuses on creating wedding ceremony truffles for {couples} within the Boston space. Her small enterprise is rising and she or he desires to maneuver her operations to an even bigger location and buy a brand new area. Earlier than she will be able to transfer her enterprise, she must borrow cash from the financial institution.
She creates a multi-step earnings assertion to indicate the financial institution how effectively her core enterprise is doing. Over the course of the 12 months, Sarah bought $80,000 price of wedding ceremony truffles. She additionally had the next bills:
- Hire: $24,000
- Utilities: $5,000
- Insurance coverage: $1,000
- Baking provides: $10,000
- Gear: $700
- Depreciation and amortization: $100
Right here’s how Sarah calculated her working earnings
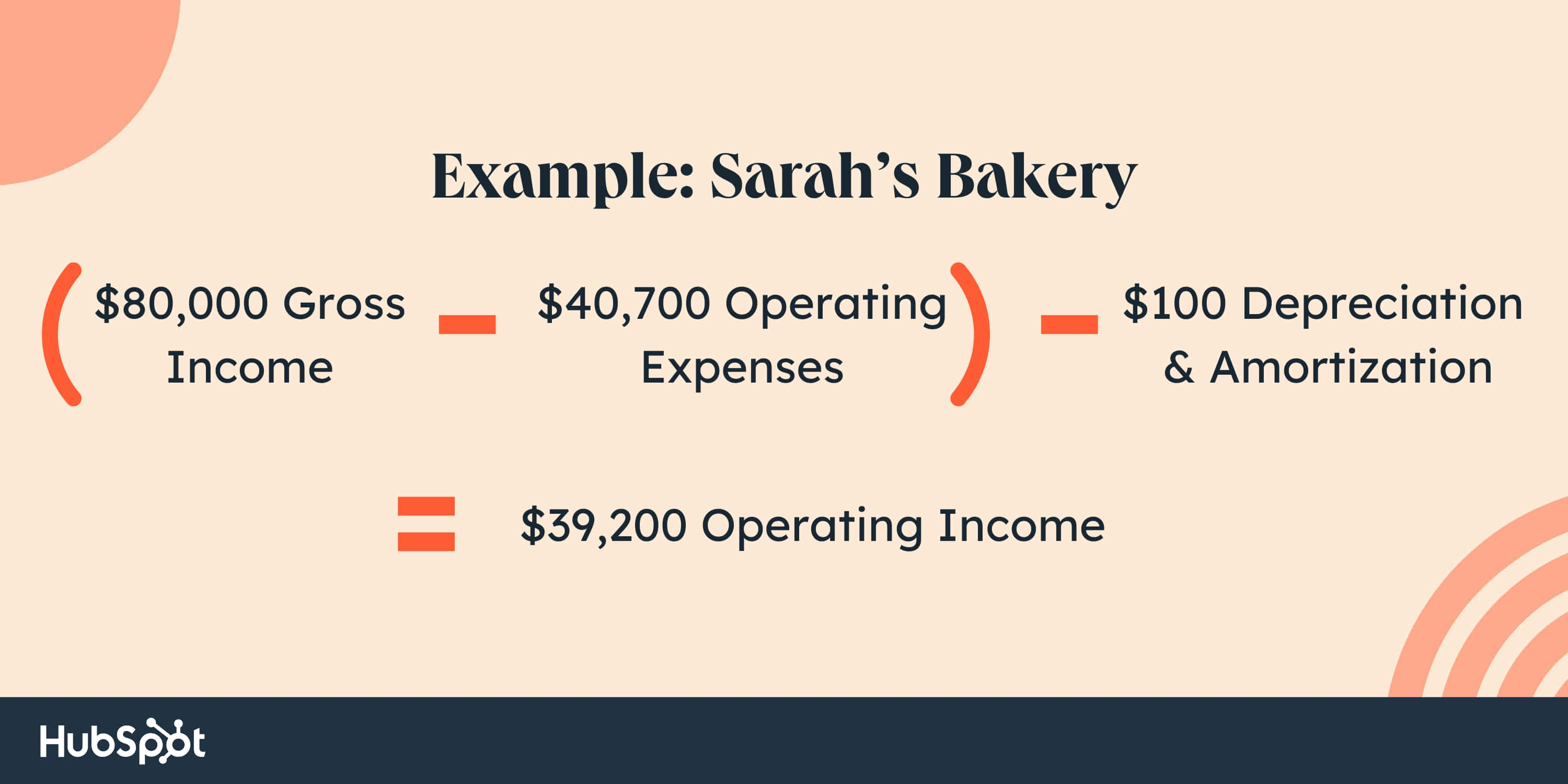
With a optimistic working earnings of $39,200, Sarah can present the financial institution she’s been capable of generate a revenue together with her enterprise. This will increase the chance she’ll get a mortgage to assist pay for the price of buying the brand new location.
Instance 2: Google
To get an thought of what this seems like, right here’s an instance of Google’s earnings assertion over the previous few years, together with working earnings.
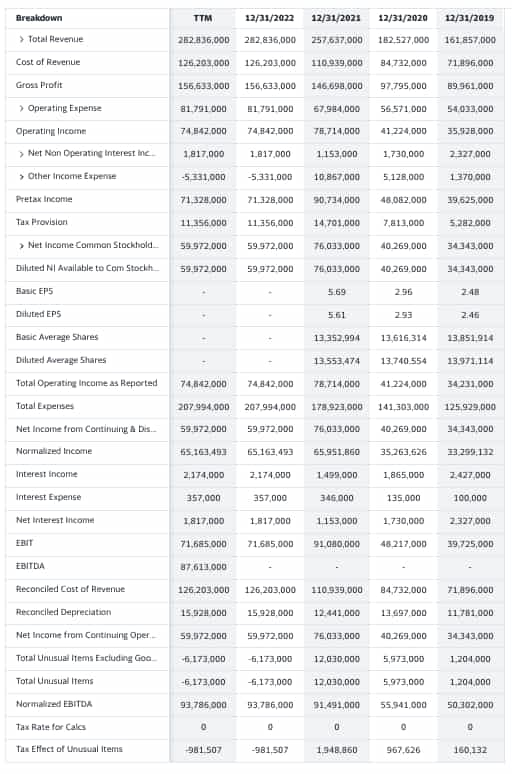
We will see that Google has maintained a optimistic working earnings over the previous 4 years. This in style search engine’s excessive working earnings is a sign of its profitability.
Understanding Your Working Revenue
With the working earnings and different measures of your small business’ money flows and monetary standing, you may gauge your small business’ means to usher in a revenue. The upper the working earnings, the extra worthwhile the corporate’s core enterprise is.


